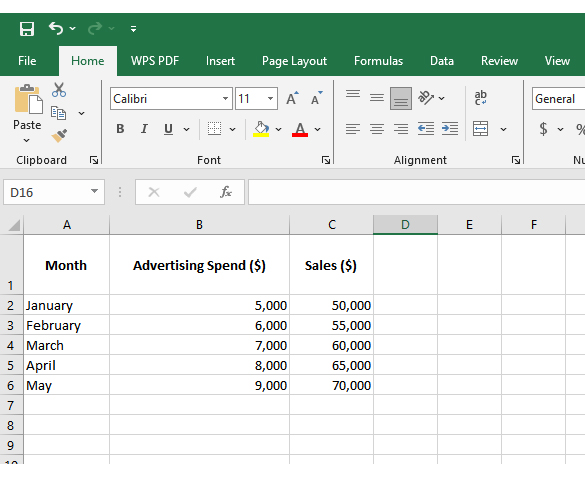
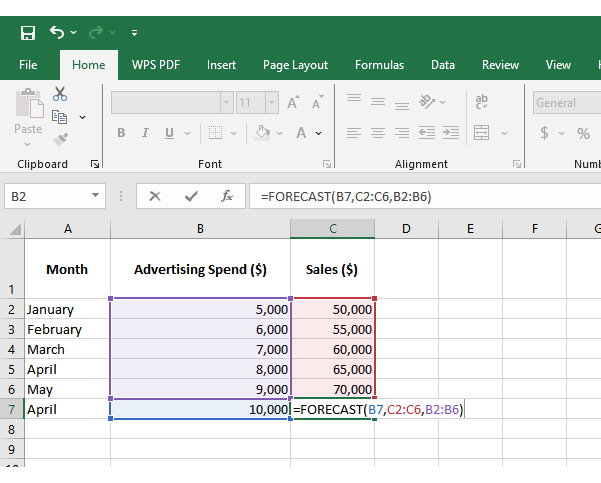
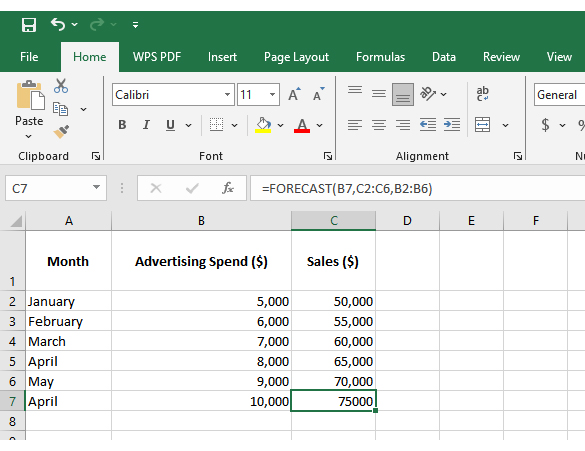
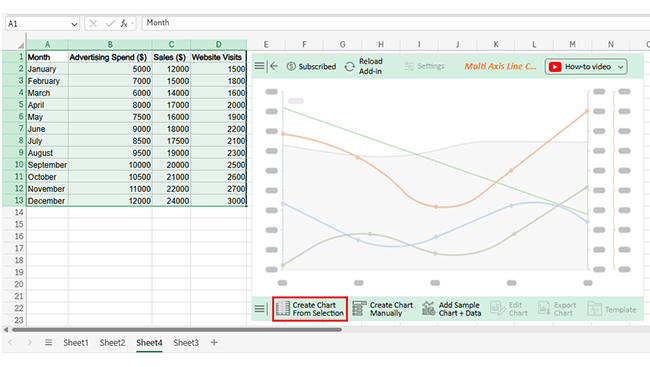
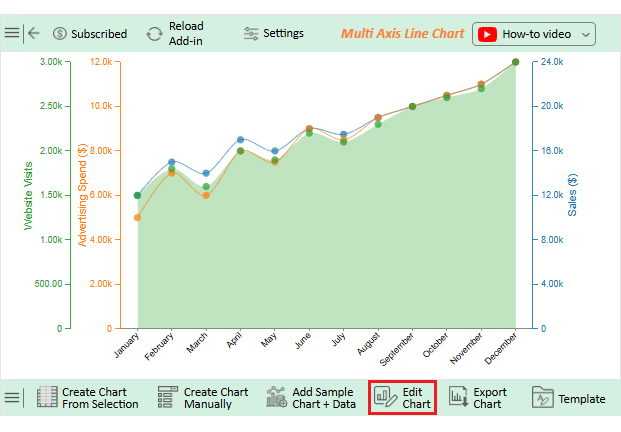
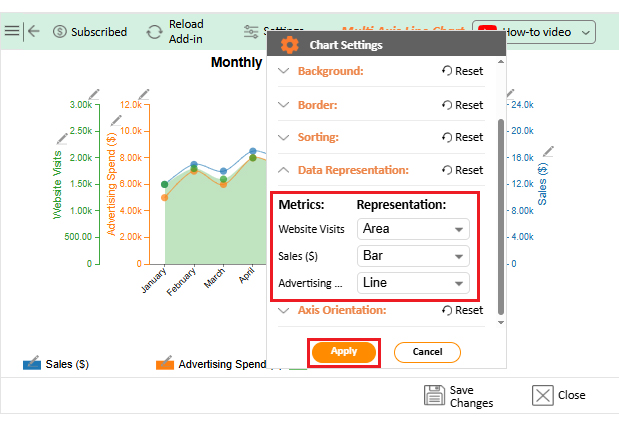
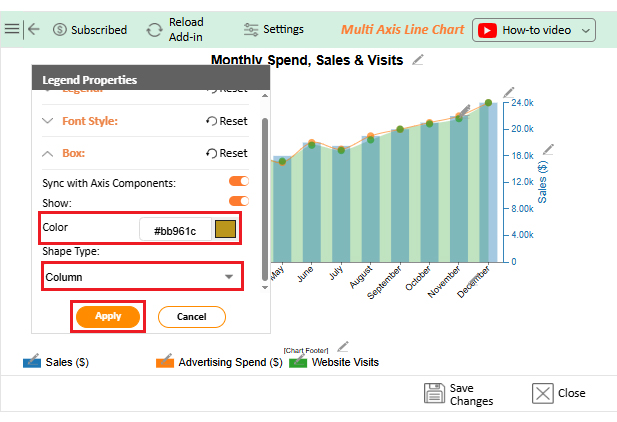
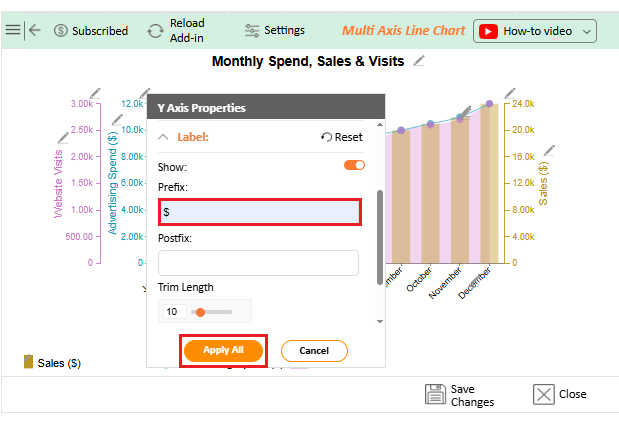
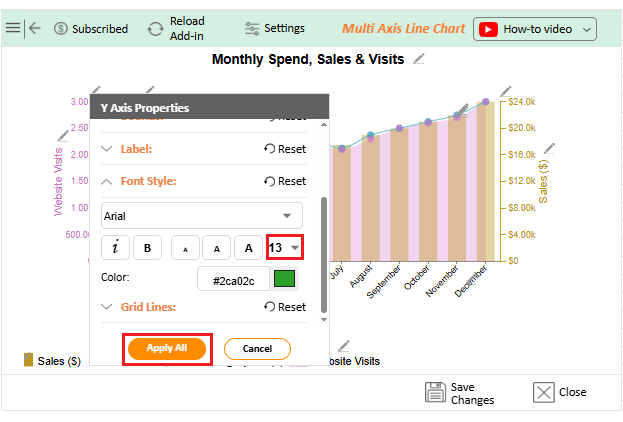
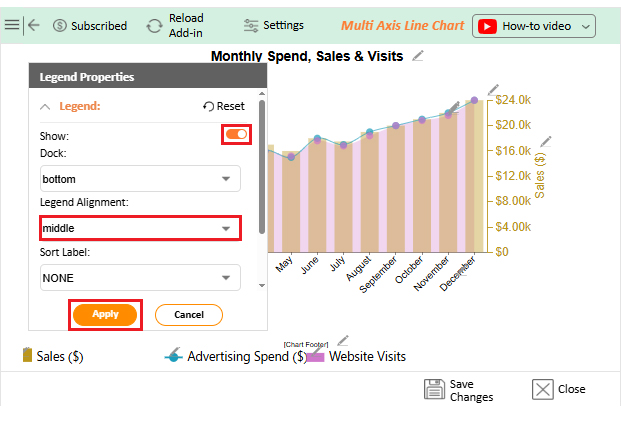
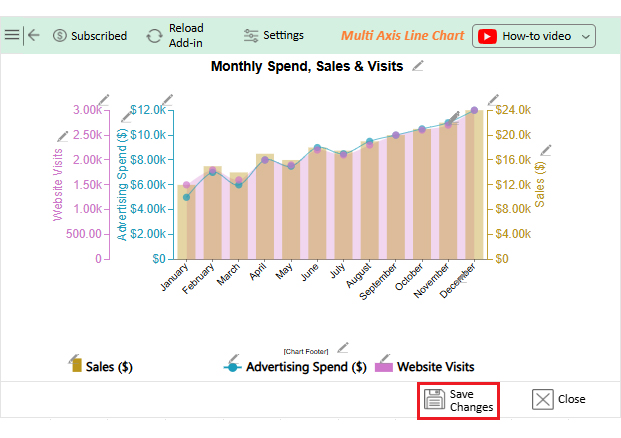
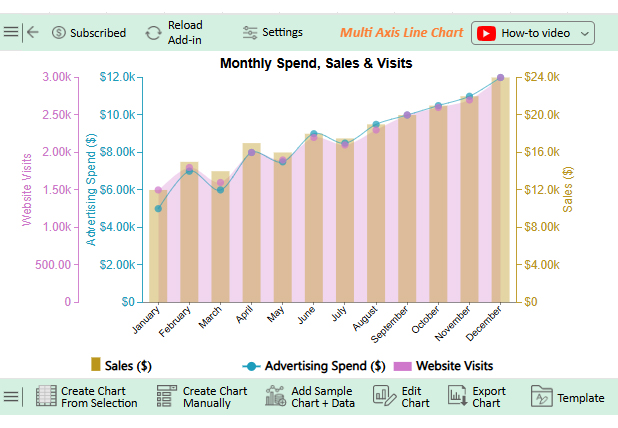
Numbers alone can seem dry, even when they reveal growth opportunities. That is why forecasting using Excel is crucial. But while Excel handles calculations effectively, its Excel charts may not always communicate the story clearly or compellingly. Subtle trends may remain hidden behind ordinary graphs.
Categories