Categories
Organizations that want better, faster decisions need to understand what sets reporting apart from analytics. Both methods use data, but they’re built to solve different problems. One summarizes outcomes, the other explains them and points to what’s coming.

This guide breaks down analytics vs reporting without fluff. You’ll see exactly when to use each approach, what makes them different, and how they fit into a solid data strategy. Whether you’re new to business intelligence or working to sharpen your team’s processes, the distinctions matter.
Definition: Reporting vs analytics starts with a simple split. Reporting takes historical data and arranges it into structured formats like dashboards or scheduled summaries. Its job is to show what’s already happened. Think performance monitoring, KPI tracking, and status updates for stakeholders.
Analytics digs deeper. It explores data to reveal patterns, connections, and the reasons behind outcomes. Rather than just displaying numbers, analytics answers the “why” and forecasts what’s ahead. This kind of work drives strategic choices and long-term planning.
The central contrast in reporting vs analysis is direction. Reporting looks back and answers “what happened.” Analytics looks forward and tackles “why did it happen” and “what should we do next.” For those just getting started, analytics vs reporting can be thought of as the gap between summary and investigation.
They’re essential tools for converting raw information into actionable intelligence. When used properly, they keep organizations both informed and ready to move on what they’ve learned.
Key reasons include:
Grasping analytics vs reporting gets easier with a clear structure.
| Aspect | Reporting | Analytics |
| Purpose | Summarize past performance | Discover insights and predictions |
| Data focus | Historical, structured data | Historical and real-time data |
| Time orientation | Past-focused | Present and future-focused |
| Level of complexity | Low to moderate | Moderate to advanced |
| User type | Executives, managers | Analysts, strategists |
| Tools commonly used | Dashboards, BI reports | Statistical and BI tools |
| Output format | Tables, charts, summaries | Insights, forecasts, models |
To fully grasp reporting and analytics, you need to know what powers them. Key components include:
Real-world scenarios clarify reporting vs analysis by showing how each gets applied.
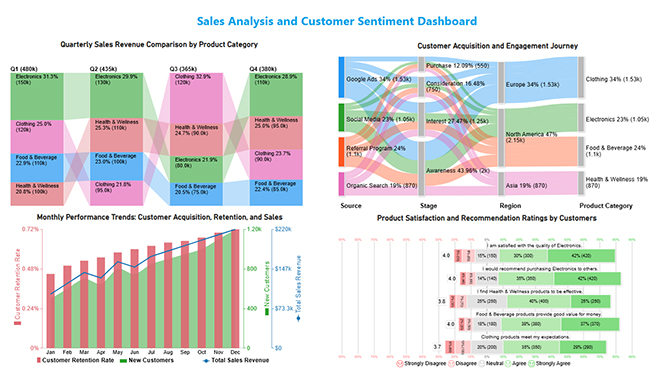
This sales analytics and customer sentiment dashboard unifies revenue performance, customer journeys, growth trends, and satisfaction insights to reveal key sales drivers and customer perceptions.
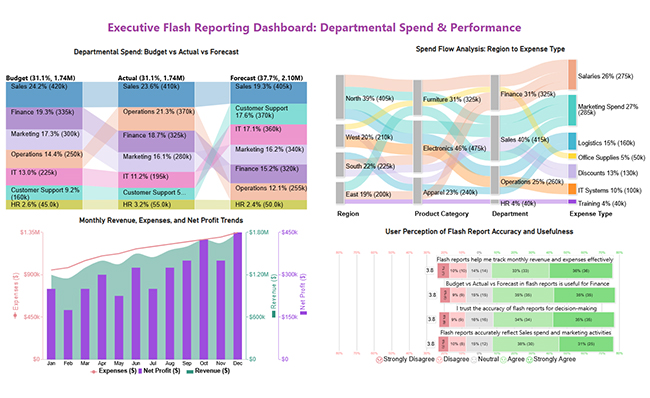
This executive dashboard gives leaders a high-level snapshot of budgets, spending, revenue trends, and user confidence for quick, informed decision-making.
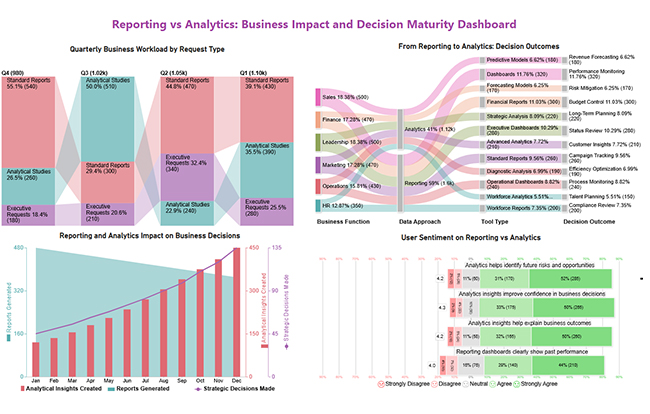
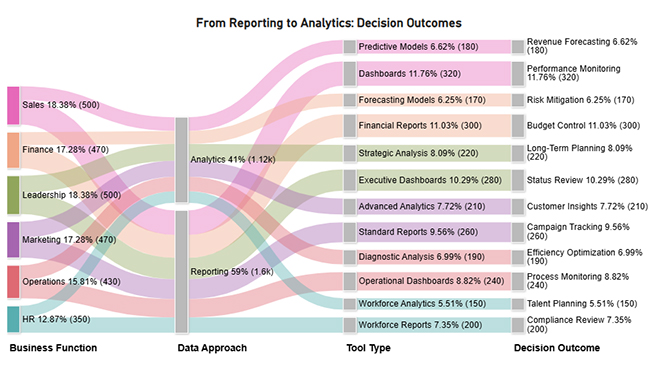
This dashboard highlights the shift from reporting to analytics, showing changing workloads, stronger decision impact, and rising confidence in analytics-driven insights.
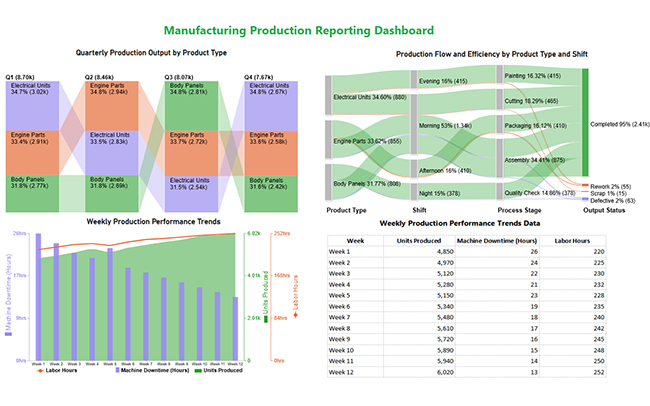
This manufacturing dashboard uses product analytics to monitor output, efficiency, downtime, and quality, helping teams optimize production and reduce losses.
Power BI delivers a strong environment for evaluating reporting vs analysis through interactive dashboards and advanced visualizations.
Why use ChartExpo?
First, Install the Power BI and Log in to Power BI.
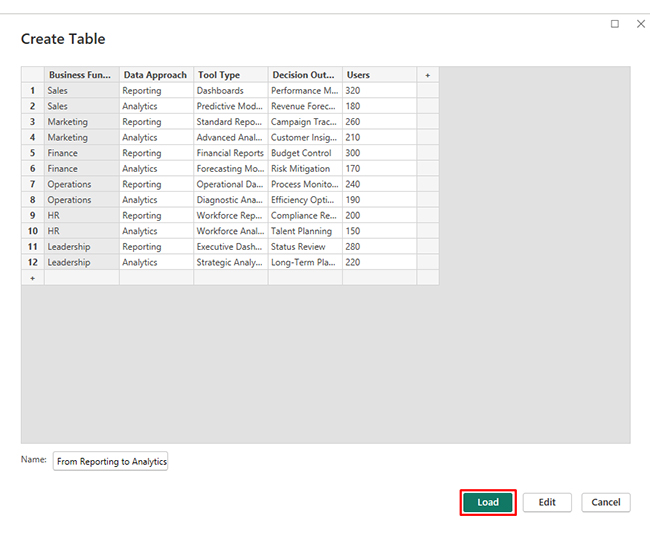
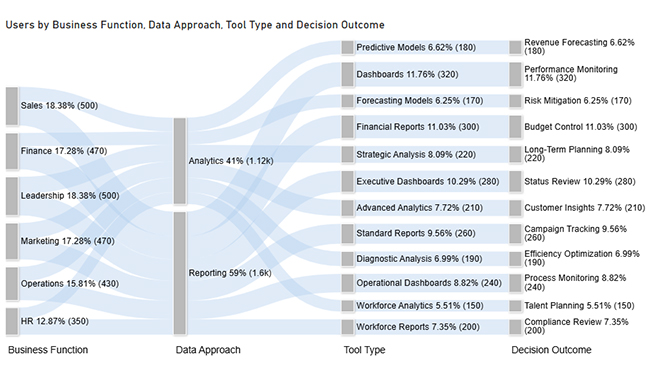
Now, consider we have the following data for a Sankey Chart.
| Business Function | Data Approach | Tool Type | Decision Outcome | Users |
| Sales | Reporting | Dashboards | Performance Monitoring | 320 |
| Sales | Analytics | Predictive Models | Revenue Forecasting | 180 |
| Marketing | Reporting | Standard Reports | Campaign Tracking | 260 |
| Marketing | Analytics | Advanced Analytics | Customer Insights | 210 |
| Finance | Reporting | Financial Reports | Budget Control | 300 |
| Finance | Analytics | Forecasting Models | Risk Mitigation | 170 |
| Operations | Reporting | Operational Dashboards | Process Monitoring | 240 |
| Operations | Analytics | Diagnostic Analysis | Efficiency Optimization | 190 |
| HR | Reporting | Workforce Reports | Compliance Review | 200 |
| HR | Analytics | Workforce Analytics | Talent Planning | 150 |
| Leadership | Reporting | Executive Dashboards | Status Review | 280 |
| Leadership | Analytics | Strategic Analysis | Long-Term Planning | 220 |
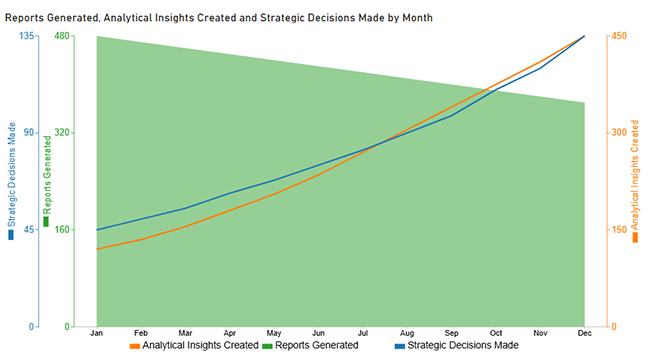
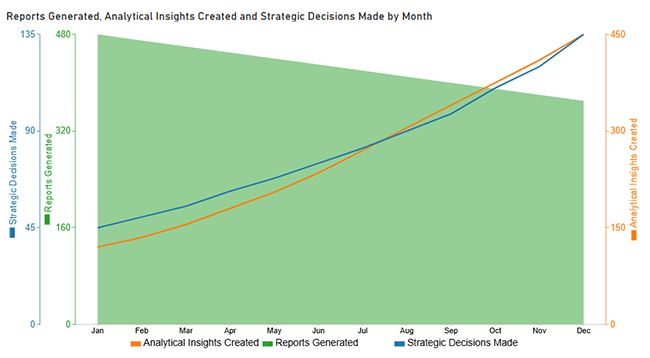
Now discuss the second chart. Consider we have the following data for the Multi Axis Line Chart.
| Month | Reports Generated | Analytical Insights Created | Strategic Decisions Made |
| Jan | 480 | 120 | 45 |
| Feb | 470 | 135 | 50 |
| Mar | 460 | 155 | 55 |
| Apr | 450 | 180 | 62 |
| May | 440 | 205 | 68 |
| Jun | 430 | 235 | 75 |
| Jul | 420 | 270 | 82 |
| Aug | 410 | 305 | 90 |
| Sep | 400 | 340 | 98 |
| Oct | 390 | 375 | 110 |
| Nov | 380 | 410 | 120 |
| Dec | 370 | 450 | 135 |
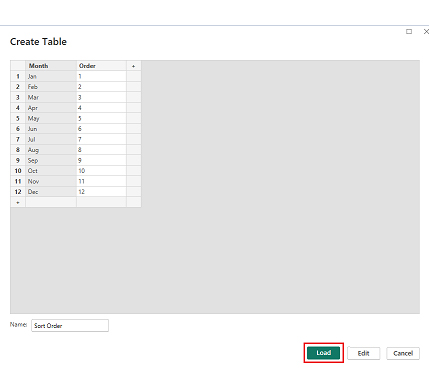
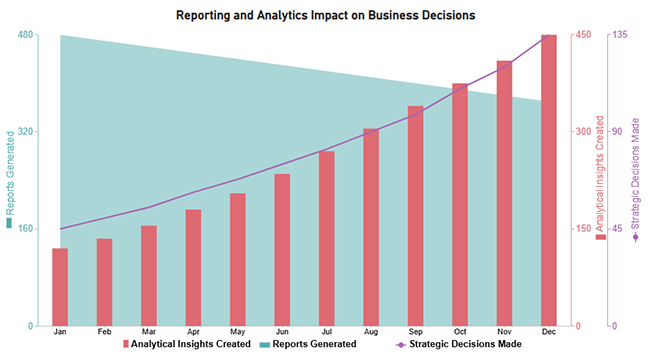
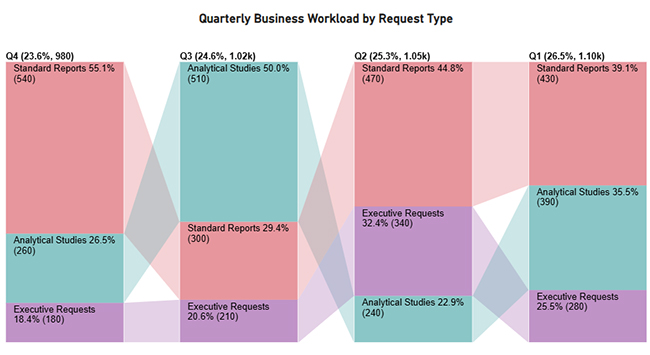
Now discus third chart. Consider we have the following data for a Comparison Bar Chart.
| Quarter | Request Type | Business Workload Volume |
| Q1 | Standard Reports | 430 |
| Q1 | Analytical Studies | 390 |
| Q1 | Executive Requests | 280 |
| Q2 | Standard Reports | 470 |
| Q2 | Analytical Studies | 240 |
| Q2 | Executive Requests | 340 |
| Q3 | Standard Reports | 300 |
| Q3 | Analytical Studies | 510 |
| Q3 | Executive Requests | 210 |
| Q4 | Standard Reports | 540 |
| Q4 | Analytical Studies | 260 |
| Q4 | Executive Requests | 180 |
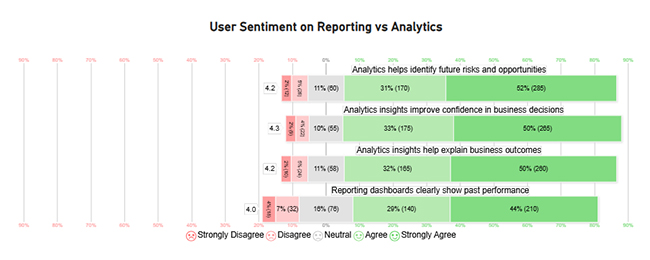
Now, discuss the fourth chart, consider we have the following data for the Likert Chart.
| Question | Scale | Responses |
| Reporting dashboards clearly show past performance | 1 | 18 |
| Reporting dashboards clearly show past performance | 2 | 32 |
| Reporting dashboards clearly show past performance | 3 | 76 |
| Reporting dashboards clearly show past performance | 4 | 140 |
| Reporting dashboards clearly show past performance | 5 | 210 |
| Analytics insights help explain business outcomes | 1 | 10 |
| Analytics insights help explain business outcomes | 2 | 24 |
| Analytics insights help explain business outcomes | 3 | 58 |
| Analytics insights help explain business outcomes | 4 | 165 |
| Analytics insights help explain business outcomes | 5 | 260 |
| Analytics helps identify future risks and opportunities | 1 | 12 |
| Analytics helps identify future risks and opportunities | 2 | 26 |
| Analytics helps identify future risks and opportunities | 3 | 60 |
| Analytics helps identify future risks and opportunities | 4 | 170 |
| Analytics helps identify future risks and opportunities | 5 | 285 |
| Analytics insights improve confidence in business decisions | 1 | 9 |
| Analytics insights improve confidence in business decisions | 2 | 22 |
| Analytics insights improve confidence in business decisions | 3 | 55 |
| Analytics insights improve confidence in business decisions | 4 | 175 |
| Analytics insights improve confidence in business decisions | 5 | 265 |
Arrange the charts efficiently and add interactivity to create a clear, engaging dashboard. After placement, the dashboard should appear as shown below.
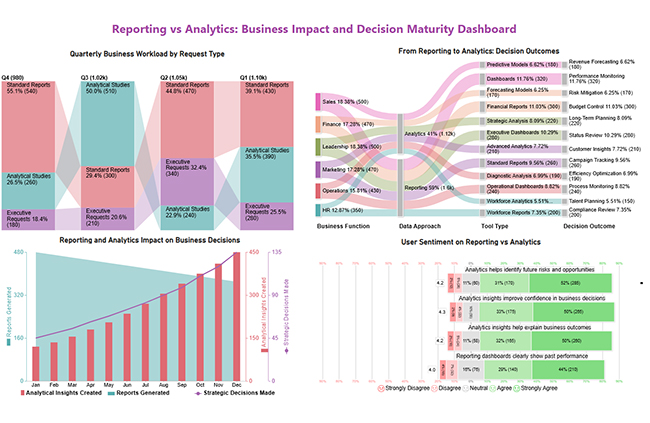
Combining reporting and analytics lets organizations balance control with innovation. Key benefits include:
Picking the right approach in reporting vs analytics depends on business objectives, data maturity, and user capabilities.
Best practices include:
Reporting works best when you need consistent summaries of past performance for monitoring KPIs and compliance.
Yes, blending reporting and analytics delivers both historical visibility and forward-looking insights.
Analytics is typically more advanced since it involves exploration, modeling, and prediction beyond static reporting.
Modern BI platforms support both analytics and reporting, letting users scale from summaries to insights within a single ecosystem.
Reporting turns raw data into clear snapshots of past performance and progress. It supports routine monitoring, compliance, and quick status checks for stakeholders. Analytics goes further, testing drivers, patterns, and relationships behind the results. Together they answer what happened, why it happened, and what to do.
Use a shared data model, then build reports and analytic views in Power BI. Add ChartExpo visuals, like Sankey and Likert, to explain flows and sentiment. Validate insights with KPIs, segment filters, and repeatable steps for decision-making. This blend improves planning, reduces risk, and highlights opportunities before they vanish. When reporting and analytics work together, teams move faster and act confidently.